
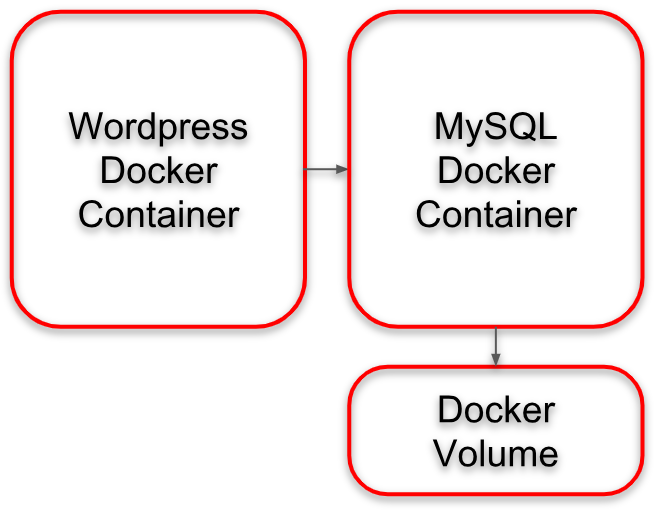
You will see why we are doing this in the next few steps.

To enable it, follow the below-mentioned steps: # nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configįind PasswordAuthentication, uncomment it and replace no with yes, as shown below.
#DOCKER HOW TO INSTALL MAVEN YUM PASSWORD#
By default, SSH password authentication is disabled in our instance. īefore moving forward, we have one last thing to do. Go to the end of the file and paste the below-mentioned line as it is. To do so, follow the below-mentioned steps: # nano /etc/sudoers Once we have created the user, it's time to grant sudo access to it, so it doesn't ask for a password when we log in as root. Passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.Ĭopy the password for user ansadmin and save it somewhere safe. Make sure that you use a strong password.
#DOCKER HOW TO INSTALL MAVEN YUM UPDATE#
Now, use the passwd command to update the ansadmin user’s password. So let’s create a user, by using the command adduser, which will create a new user to our system: # useradd ansadmin The first thing we are going to do is create a user named ansadmin, as it is considered the best practice.
Through the above command, we notice that the config file path is missing, which we will create and configure later. Once the installation is complete, verify: # ansible -versionĬonfigured module search path = Īnsible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible It might take a minute or two to complete the installation, so sit tight. Use the below-mentioned command to do so: # sudo yum updateĪfter Python is installed on the system, use pip2 command to install Ansible on the Control Node: # sudo pip2 install ansible To install Ansible, we are going to use python2-pip, and to do so, first, we have to install python2. Here we are using CentOS 8 as our Ansible Control Node. Let us begin the guide by installing Ansible on our Control node. To overcome this limitation, Ansible plays an integral part as a shell script executor, which enables Jenkins to execute the workflow of a process. Still, sometimes, it gets overwhelming to maintain the application's status, and script reusability becomes harder as the project grows. In the world of CI/CD process, Jenkins is a popular tool for provisioning development/production environments as well as application deployment through pipeline flow. Let’s dig into how to install the right version, which works on RHEL 8.In this guide, we will use Ansible as a Deployment tool in a Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment process using Jenkins Job. To be fair, the upstream Docker CE docs also demonstrate how to install the version made for CentOS 7, so it’s kind of understandable that they are wrong on.
It demonstrates how to install the version for CentOS 7, not CentOS 8 (which does work). This article shows the user how to install the wrong version of Docker-CE.If you’d read closely, you might have read a false statement which says, “What version to install? Well, Red Hat seems to have somehow blocked the installation of containerd.io > 1.2.0-3.el7, which is a dependency of docker-ce.” This statement is completely wrong. If you’ve searched google to figure out how to install Docker-CE on RHEL 8, you may have been led to this very popular article: : How to Install Docker on RHEL 8.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
